Breaking Up Google? How DOJ's Antitrust Proposal Could Reshape Big Tech
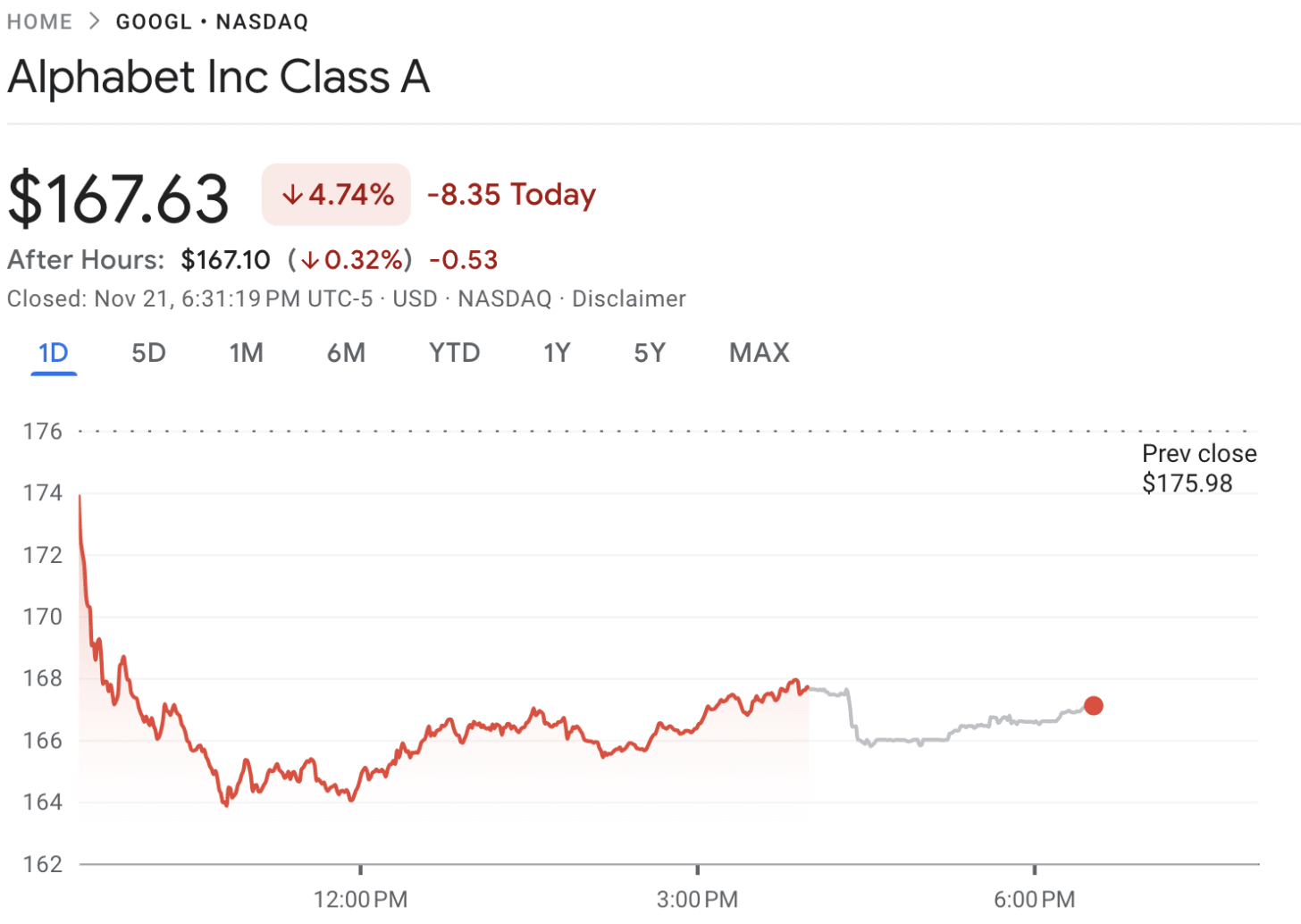
Shares of Google parent company Alphabet dropped nearly 6.5% after the DOJ proposed aggressive antitrust remedies, including a potential divestment of Chrome, which could impact Google’s search dominance and its generative AI capabilities.
The DOJ's proposal seeks to restrict exclusive deals with companies like Apple and Samsung, and suggests splitting off key assets like Android, which are central to Google’s ecosystem and AI-driven services.
The regulatory actions come amidst speculation about future leadership at the DOJ and potential policy shifts, with some hoping the next administration may take a less aggressive stance on regulating big tech companies like Google.
The market has reacted sharply to the news of proposed antitrust measures targeting Google’s parent company, Alphabet. Shares of the tech giant plunged nearly 6.5% following the revelation of one of the most aggressive antitrust remedies seen in recent years, which includes the potential divestment of its flagship browser, Chrome.
This development signals a critical moment for both Google’s dominance in search engines and its positioning in the rapidly growing generative AI space. The scope of the proposal by the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) has raised significant concerns, not only regarding Google's current market position but also the long-term impact on its future technological innovations and competitive edge.
Understanding the Antitrust Proposal
The Department of Justice (DOJ) is conducting an antitrust investigation into Alphabet, focusing on the company’s long-standing dominance in the search engine market and its alleged anti-competitive practices. The investigation examines the impact of Google’s business practices, such as exclusive agreements with device manufacturers like Apple and Samsung, and the company’s control over essential assets like Chrome and Android. The DOJ argues that these practices restrict consumer choice by limiting competition in both search and mobile operating systems. If the proposed remedies are implemented, such as the potential breakup of key assets, Google’s operational dynamics would be drastically altered.
One of the most significant consequences of this investigation is the potential divestment of Chrome, one of Google’s most valuable assets. Chrome is not just a browser; it is deeply embedded in Google’s broader ecosystem. It feeds data across multiple services, such as Google Maps, Gmail, and Calendar, making it a central hub for the company’s operations. A breakup of Chrome would effectively remove a critical component that has helped Google maintain its dominant position in the search engine market, along with its ability to innovate in areas like generative AI.
Breaking up Chrome would also have severe implications for Google’s artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities. Chrome is integral to how Google’s AI systems operate, as it gathers user data across devices to create a seamless experience. This data integration enables Google’s AI agents to deliver personalized recommendations and predictions, enhancing their functionality. Without Chrome’s data synergy, Google’s AI models could be significantly hindered, which could put the company at a considerable disadvantage when competing with other tech giants in the AI race.
In addition to the loss of Chrome’s integration, this breakup would impact the overall user experience, which relies heavily on the data and continuity provided by Google’s ecosystem. The breakup could slow down Google’s advancements in AI, especially as it seeks to leverage its integrated platforms to compete with companies like Microsoft and Amazon, which are also heavily investing in AI. As the regulatory landscape evolves, Google will need to rethink its approach to maintaining dominance in both search and AI, all while navigating an increasingly complex legal environment.
Impact on Google’s Competitive Edge in Generative AI
Generative AI, which focuses on creating content and solving complex problems through artificial intelligence, has become a key battleground among tech companies. Google has been at the forefront of this technology, leveraging its vast resources and extensive data troves to train and deploy generative AI systems. However, the Department of Justice (DOJ) has proposed breaking up Chrome and forcing Google to divest certain AI-related technologies, which could severely impact the company’s ability to maintain its competitive advantage in this rapidly growing field.
Chrome plays a crucial role in Google’s data collection infrastructure. The browser collects valuable information on users' browsing habits, search history, calendar events, and locations, all of which feed into Google’s AI systems. The more data Google has, the better its generative AI models can perform, providing highly accurate and personalized results. This interconnected system gives Google a significant edge over competitors such as Microsoft and OpenAI. Removing Chrome’s integration with other Google services would undermine this synergy, making it more challenging for Google to refine and enhance its AI models.
The potential harm to Google’s AI capabilities is further magnified by the growing importance of generative AI across various industries. From natural language processing to image generation and automated decision-making, the companies that lead in generative AI will hold a distinct competitive advantage in the coming years. Google's ability to maintain its leadership position in AI could be jeopardized if its access to user data via Chrome is limited, potentially hindering its capacity to innovate and improve its generative AI systems.
In this context, the DOJ’s proposed breakup of Chrome could fundamentally alter the trajectory of Google's AI ambitions. If regulators move forward with these plans, Google’s ability to remain competitive in the generative AI race will be significantly impacted, forcing the company to reevaluate its strategies and adapt to an environment where access to user data is increasingly restricted. This shift could have long-term consequences for Google's market leadership in both AI and search technologies.
The Larger Context of Antitrust and Big Tech
The proposed antitrust measures against Google are part of a broader effort by regulators to curb the power of Big Tech. Companies like Alphabet, Amazon, Apple, and Facebook have faced increasing scrutiny due to their market dominance and the impact their business practices have on competition. Regulators are particularly concerned about two issues: the sheer scale of these companies, which makes it difficult for smaller competitors to challenge them, and their business practices, such as exclusive contracts and self-preferencing, which are seen as anticompetitive.
In the case of Google, the company’s dominance in the search engine market, along with its integrations across mobile, cloud, and AI platforms, has raised significant concerns among regulators. Google’s control over vast amounts of user data, coupled with its extensive market reach, has led many critics to argue that the company has an unfair advantage over competitors. The Department of Justice (DOJ) has responded by proposing measures such as stopping Google from entering into exclusive deals with major companies like Apple and Samsung, or even forcing a breakup of its Android and Chrome operations.
However, the timing of these proposals is raising further questions. As government agencies grapple with the growing influence of Big Tech, there is ongoing debate about whether breaking up these companies is the most effective solution. While some believe that the current administration’s regulators are too aggressive in pursuing antitrust actions, others argue that without intervention, monopolistic practices by these companies could stifle innovation and competition, making it harder for new players to emerge in the market.
The Biden administration has shown a willingness to take a strong stance on antitrust actions against Big Tech, as demonstrated by its approach to Google. However, the situation remains uncertain, especially with the potential for a political shift. President-Elect Trump’s administration, for example, has previously suggested that the government should adopt a more hands-off approach to regulating the tech industry. This political uncertainty could influence how these antitrust cases unfold and whether the proposed remedies are ever fully implemented.
Broader Economic and Market Impact
The news of Alphabet’s potential breakup sent shockwaves through the stock market, resulting in billions of dollars being wiped off the company’s market capitalization. The broader tech market also felt the impact, with other Big Tech stocks experiencing declines in response to the antitrust scrutiny faced by Google. This highlights the larger economic consequences that regulatory actions can have on these companies, as the potential for breakups or severe penalties raises doubts about their future profitability and growth prospects.
The stock market’s reaction emphasizes the significant role that regulatory uncertainty plays in tech investments. When companies like Google face the threat of antitrust actions, their ability to innovate and expand can be severely impacted. Investors, wary of the potential long-term consequences of these regulatory pressures, may reassess the value of these tech giants. As a result, stock prices are affected, reflecting concerns about the sustainability of these companies in a more regulated environment.
For companies involved in the rapidly developing field of generative AI, the stakes are particularly high. As the sector is still in its early stages and poised for significant growth in the coming years, any regulatory actions that limit competition or reduce the resources available to companies like Google could have far-reaching consequences. These restrictions could hinder innovation, making it more difficult for these companies to maintain their leadership in AI development and affecting the overall progress of the industry.
The broader implications for emerging technologies are also significant. If antitrust measures limit the ability of companies like Google to access data and resources, it could slow the pace of innovation in fields like AI, cloud computing, and other cutting-edge technologies. This could ultimately reshape the competitive landscape, with smaller or newer companies having to navigate a more challenging environment, potentially stalling the growth of breakthrough technologies that could drive the next generation of innovation.
The Role of Policy and Future Outlook
As the regulatory landscape for Big Tech evolves, government policy will play a crucial role in shaping the future of the tech industry. The Biden administration’s aggressive approach to antitrust has set a precedent, but the outcome of future elections could significantly influence the direction of antitrust regulation. A potential shift in political power could alter the tone of regulation, particularly if a Trump administration adopts a more lenient stance toward Big Tech.
Historically, Trump’s approach to regulating Big Tech has been more hands-off, and if he returns to power, this could result in less scrutiny, especially if it benefits major tech donors. This shift might allow influential figures like Elon Musk to acquire key assets such as Chrome, further consolidating control over the tech ecosystem. Such a move could be seen as rewarding political supporters and result in a regulatory environment that favors maintaining the dominance of select tech players rather than pursuing efforts to break them up.
In addition, the leadership of agencies like the DOJ and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) will play a crucial role in determining the direction of antitrust policy. Brendan Carr, a commissioner at the FCC, has been notably antagonistic toward Big Tech, signaling that regulatory pressure on these companies is unlikely to ease in the near future. However, as the market adapts to the evolving regulatory environment, it’s possible that some proposed measures may be softened or restructured with new leadership. This uncertainty regarding leadership and policy direction is an important factor for companies like Google to consider, as it directly impacts their strategic planning and operations.
For companies like Google, navigating this uncertainty will require strategic adaptability. As antitrust measures evolve, tech giants may need to rethink their business models, particularly in areas like generative AI, where competition is intensifying. The challenge will be balancing innovation with regulatory compliance, ensuring that they can continue to lead in the AI race without violating antitrust laws. The growing influence of AI and continued regulatory scrutiny will require companies to align their strategies with the evolving legal frameworks, as the future of Big Tech depends on their ability to navigate this complex landscape.
Conclusion
The proposed antitrust measures against Google, including the potential breakup of Chrome and other key assets, represent a crucial turning point for both the company and the broader tech industry. These changes could significantly undermine Google's dominance in the search market and present a substantial challenge to its future in generative AI. As regulators continue to focus on Big Tech, the impact of these actions will reverberate across the market, affecting not only the companies directly involved but also the wider economic landscape.
With political shifts on the horizon and regulatory uncertainty ahead, the future of Google and other tech giants is unclear. This makes it a pivotal time for investors, policymakers, and industry leaders to closely monitor developments. The evolving regulatory environment will likely shape the trajectory of these companies and their ability to navigate the challenges posed by both antitrust measures and the rapidly advancing AI sector.